The generator – an inconspicuous component in the engine compartment, yet it plays a crucial role in the functionality of every vehicle. But how is a generator actually constructed, and which components enable electricity generation while driving? In this article, we delve deep into the world of generators and explain everything you need to know about the “anatomy of car generators.”
What is a Generator and What Does it Do?
Think of the generator as a small power plant in your car. Its job is to recharge the battery while driving and ensure the operation of all electrical consumers, such as lights, radio, or air conditioning. Without a functioning generator, your vehicle would simply stop after a short time.
How a Generator Works: From Mechanical Energy to Electrical Power
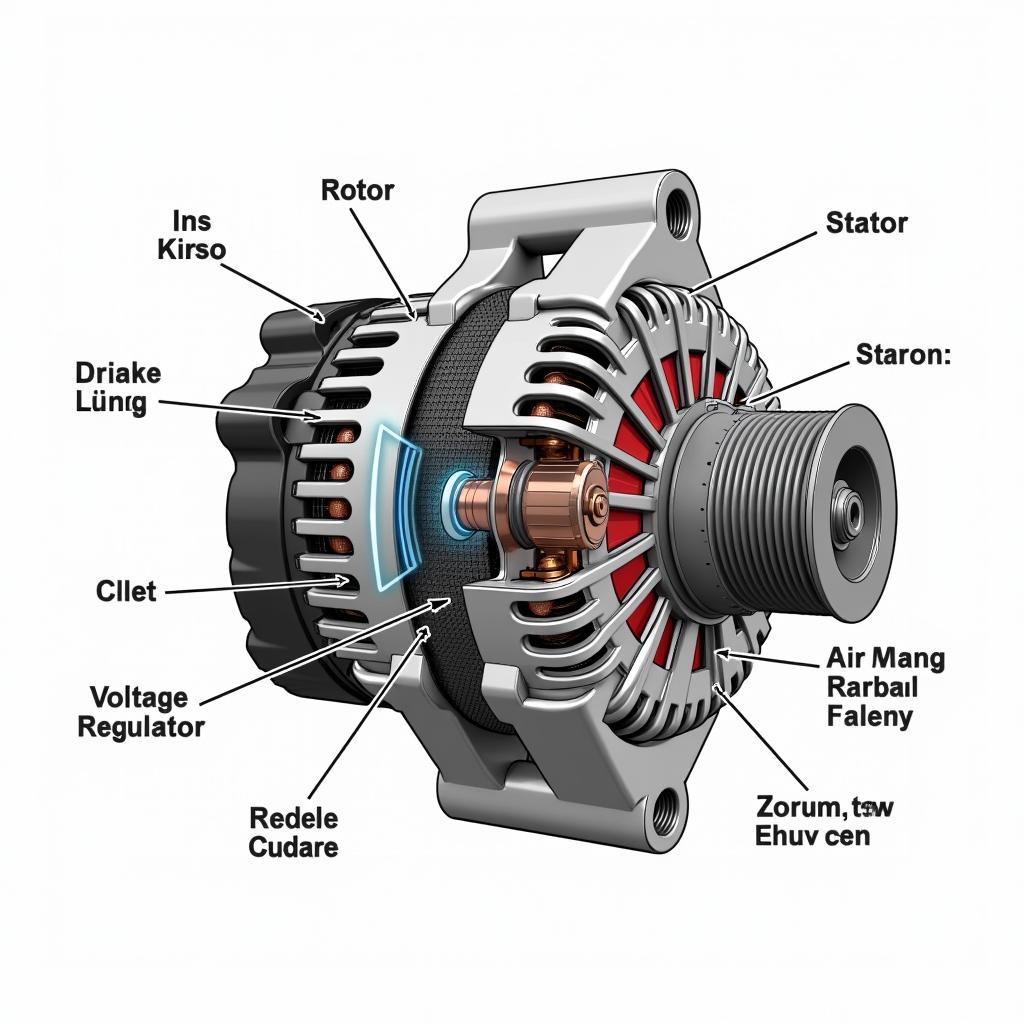 Diagram illustrating the components of a car generator.
Diagram illustrating the components of a car generator.
The functionality of a generator is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. In short: Mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. The generator is driven by a belt connected to the crankshaft of the engine. This belt sets the rotor, which rotates inside the stator, in motion.
The rotor is essentially an electromagnet through which a direct current flows. By rotating the rotor within the stator, which consists of several coils, an alternating current is induced in these coils. This alternating current is then converted into direct current by the diode bridge, which can then charge the battery and supply the electrical consumers.
Components of a Generator at a Glance
A generator consists of several components that work together precisely to ensure electricity generation:
Rotor
- Rotating electromagnet that is driven by the engine’s rotation.
- Generates a magnetic field that enables current induction in the stator.
Stator
- Stationary part of the generator, consisting of several coils.
- An alternating current is induced in the coils by the rotating magnetic field of the rotor.
Diode Bridge (Rectifier)
- Converts the alternating current generated in the stator into direct current.
- Ensures that the current flows in the correct direction to charge the battery.
Voltage Regulator
- Regulates the voltage of the current generated by the generator.
- Prevents overvoltages and thus protects the battery and electrical consumers.
Pulley
- Transmits the rotational motion of the engine to the rotor.
Slip Rings (Brushes)
- Enable the transfer of current from the rotor to the stator.
Common Problems and Sources of Errors in Generators
Although generators are generally very reliable, they can occasionally cause problems. Typical sources of error are:
- Wear of the slip rings (brushes)
- Defective diode bridge
- Failure of the voltage regulator
- Defective bearings in the generator
Advantages of a Properly Functioning Generator
A properly functioning generator is essential for the reliability of your vehicle. The advantages include:
- Reliable power supply for all electrical consumers
- Constant battery charging while driving
- Prevention of starting difficulties
What to Consider When Buying a New Generator?
If your vehicle’s generator is defective, replacement is unavoidable. When buying a new generator, pay attention to the following points:
- Compatibility with your vehicle model
- Quality of the generator (prefer known manufacturers)
- Warranty
Conclusion
The generator plays a central role in the functionality of every vehicle. A basic understanding of its structure and function is therefore essential for every car owner. If you have problems with the generator, you should always contact a specialist workshop.
Further Questions on the Topic of “Generator Anatomy”:
- How can I check my car’s generator myself?
- What is the average lifespan of a generator?
- What does it cost to replace a generator?
- Are there differences between generators for gasoline and diesel vehicles?
Visit our blog at autorepairaid.com for more exciting articles about cars and repairs. If you have any questions, our team of experts is happy to help – simply contact us via our website!

