Every driver is familiar with it: the stopping distance rule of thumb. But how exactly does it work, and what should you consider when calculating braking distance? This article provides a comprehensive overview of the “Stopping Distance Rule of Thumb” and explains why it can save lives in an emergency.
What Does the “Stopping Distance Rule of Thumb” Mean?
The “Stopping Distance Rule of Thumb” is a simple formula used to roughly estimate a vehicle’s stopping distance. It states: Stopping Distance = Reaction Distance + Braking Distance.
- Reaction Distance: The distance the vehicle covers while the driver is still reacting, from recognizing a hazard to applying the brakes.
- Braking Distance: The distance the vehicle needs from applying the brakes until coming to a complete stop.
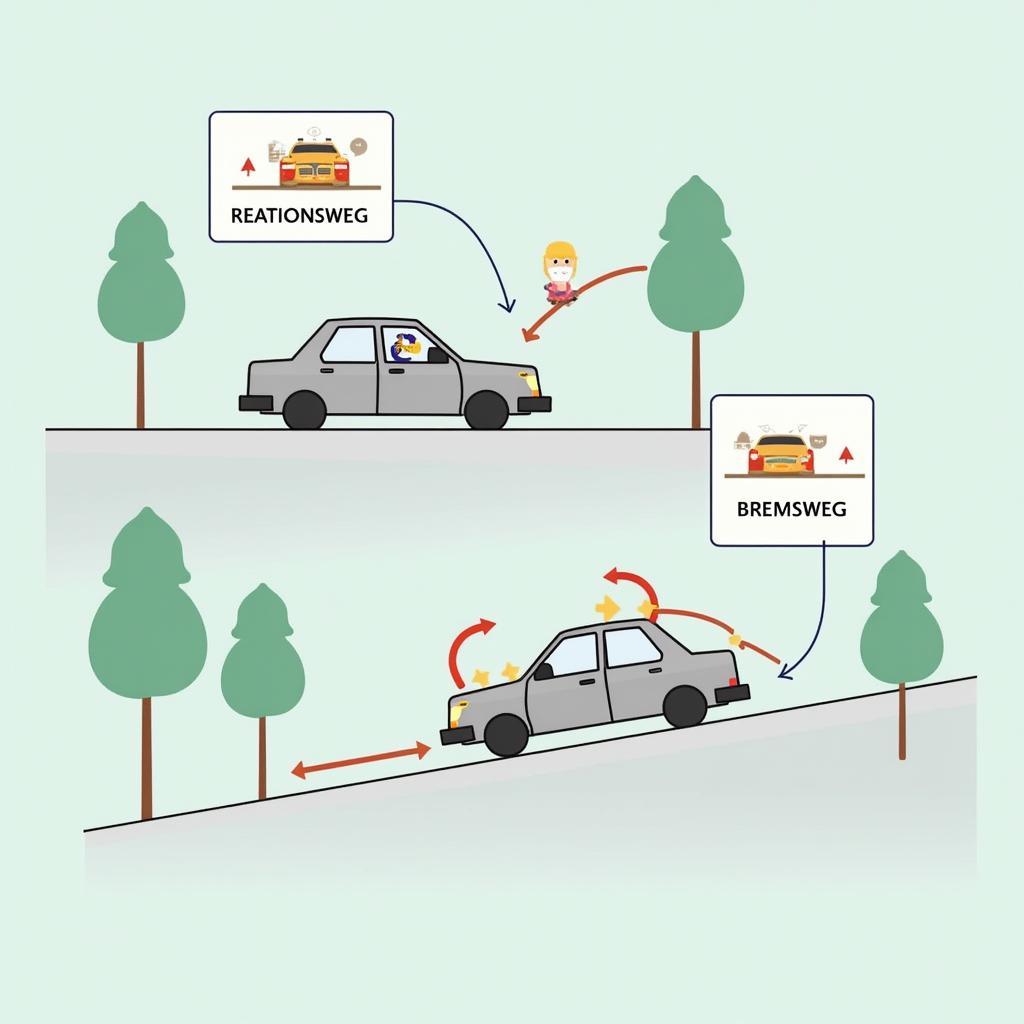 Diagram illustrating reaction distance and braking distance
Diagram illustrating reaction distance and braking distance
The Rule of Thumb in Detail
There are two common methods for calculating stopping distance using the rule of thumb:
1. Method: Calculating with Speed
- Reaction Distance: Speed divided by 10 and multiplied by 3 (Example: 50 km/h / 10 x 3 = 15 meters reaction distance)
- Braking Distance: Speed divided by 10, the result squared (Example: 50 km/h / 10 = 5, 5 x 5 = 25 meters braking distance)
2. Method: Using “Half Speedometer Values”
- Reaction Distance: Read the speed and halve the value (Example: 50 km/h, halved gives 25 meters reaction distance)
- Braking Distance: Read half the speed and multiply this value by itself (Example: Half of 50 km/h is 25, 25 x 25 = 625, the last two digits give 25 meters braking distance)
Although both methods yield different results, they serve only as a rough guide.
Factors Influencing Stopping Distance
The actual stopping distance can differ greatly from the rule of thumb calculation. Various factors play a role:
- Vehicle Condition: Worn tires, faulty brakes, or a poorly maintained suspension significantly extend braking distance.
- Road Surface Condition: Wet, slippery, or dirty roads significantly increase braking distance compared to dry and clean roads.
- Weather Conditions: Rain, snow, or black ice further extend braking distance.
- Driver Condition: Fatigue, distraction, or the influence of medication or alcohol impair the driver’s reaction time, thus extending reaction distance.
 Diagram showing factors influencing stopping distance
Diagram showing factors influencing stopping distance
Why Is the Stopping Distance Rule of Thumb Important?
Although the “Stopping Distance Rule of Thumb” may be imprecise, it highlights the importance of maintaining a safe distance in traffic. It shows that stopping distance doesn’t depend solely on braking distance but significantly on the driver’s reaction time as well.
Especially in critical situations, such as the sudden appearance of pedestrians, cyclists, or obstacles on the road, knowing about stopping distance can save lives.
Tips for Safe Braking:
- Always maintain a safe following distance – including and especially in difficult weather conditions.
- Pay attention to your vehicle’s condition and have your brakes and tires checked regularly.
- Avoid distractions while driving, such as using your phone or eating.
- Adjust your speed to the prevailing conditions.
Conclusion
The “Stopping Distance Rule of Thumb” is a useful tool for roughly estimating braking distance. However, keep in mind that the actual stopping distance depends on many factors. Drive defensively, maintain a safe following distance, and ensure your vehicle is in perfect condition to come to a stop in time in an emergency.
Do you have questions about car repair or need technical assistance? Feel free to contact us via our website autorepairaid.com. Our experts are happy to assist you with advice and support.

