The particulate filter, also known as the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF), is an important component of modern diesel vehicles. Its task is to filter harmful soot particles from exhaust gases, thereby reducing environmental pollution. But how exactly is a particulate filter structured? What problems can occur and how can they be solved? In this article, you will learn everything worth knowing about the structure and function of the particulate filter.
What is a Particulate Filter and How is it Structured?
A particulate filter is a specially designed filter installed in the exhaust stream of diesel engines. It consists of a honeycomb ceramic monolith whose channels are alternately blocked. This structure forces the exhaust gases to flow through the porous walls, retaining the soot particles in the filter.
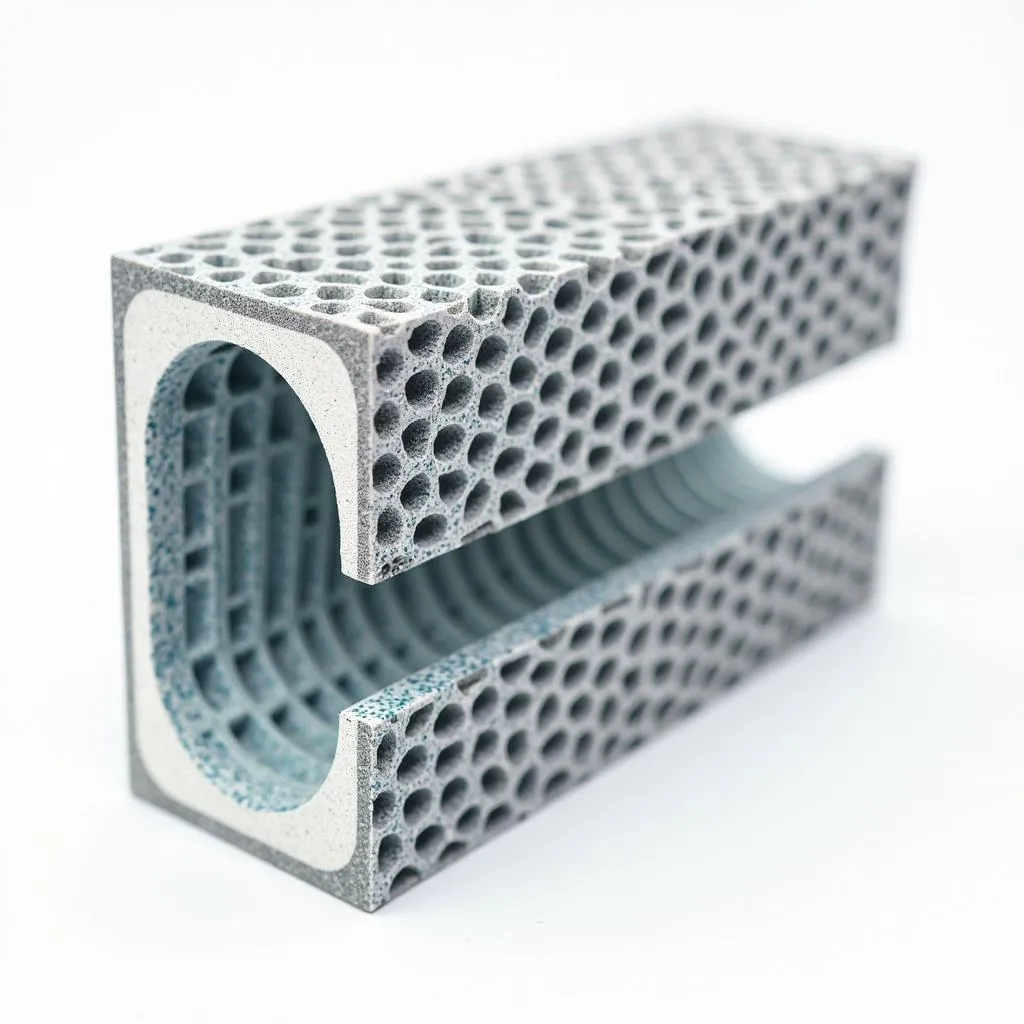 Diagram showing the internal structure of a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
Diagram showing the internal structure of a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
“A well-functioning particulate filter can remove up to 98% of soot particles from exhaust gases,” explains Dr. Ing. Markus Schmidt, an expert in exhaust aftertreatment systems. “This is an important contribution to improving air quality, especially in cities.”
How the Particulate Filter Works
The particulate filter operates in two phases: filtration and regeneration. During the filtration phase, soot particles are retained in the filter while exhaust gases flow through the porous walls. Over time, soot accumulates in the filter, increasing back pressure in the exhaust system. To prevent the filter from clogging, it must be regenerated regularly.
Regeneration occurs through the controlled combustion of the collected soot. This involves increasing the exhaust temperature through various measures, such as fuel post-injection into the exhaust stream. At high temperatures, the soot burns into ash, which remains in the filter.
Common Problems with the Particulate Filter
Although the particulate filter is a robust component, problems can occur over time.
- Clogged Particulate Filter: Frequent short trips or a faulty engine control unit can lead to incomplete regeneration and thus a clogged filter.
- Faulty Sensors: The regeneration of the particulate filter is controlled by various sensors that can fail over time.
- Mechanical Damage: The filter can be damaged by external factors, such as stone chips.
 Mechanic diagnosing a problem with a Diesel Particulate Filter
Mechanic diagnosing a problem with a Diesel Particulate Filter
“A clogged particulate filter often manifests as a loss of power, increased fuel consumption, or illuminated warning lights,” warns Master Mechanic Sarah Bauer. “In such cases, you should visit a repair shop immediately.”
Solutions for Particulate Filter Problems
Repairing a faulty particulate filter can be costly. Therefore, it is advisable to take preventative measures to extend the filter’s lifespan.
- Regular Maintenance: Have your particulate filter regularly inspected and serviced by a qualified workshop.
- Adjust Driving Style: Avoid frequent short trips and regularly allow the engine to reach operating temperature.
- Use High-Quality Fuel and Oil: High-quality fuels and oils contain fewer additives that can contribute to soot formation.
Conclusion
The particulate filter is an essential component of modern diesel vehicles that makes an important contribution to reducing harmful emissions. Through regular maintenance and an adapted driving style, you can extend the lifespan of your particulate filter and avoid expensive repairs. If you experience problems with the particulate filter, you should visit a qualified workshop immediately.
Other Interesting Topics Related to Vehicle Technology
- EGR Valve: Function, Problems, and Cleaning
- Turbocharger: How it Works and Common Faults
- Engine Control Unit: Functions and Troubleshooting
Visit our website autorepairaid.com for more helpful information and tips on car repair. Our experts are happy to assist you with any questions!